Некоммерческое акционерное общество
АЛМАТИНСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ ЭНЕРГЕТИКИ И СВЯЗИ
Кафедра иностранных языков
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК
Методические указания для развития навыков перевода научно-технических текстов (для студентов специальности 5В070400 – «Вычислительная техника и программное обеспечение »)
Алматы 2011
СОСТАВИТЕЛЬ: Ж.Б.Ержанова. Английский язык. Методические указания для развития навыков перевода научно-технических текстов (для студентов специальности 5В070400) – Алматы; АУЭС, -2011-35 с.
В методических указаниях рассматриваются основы перевода, лексические трудности перевода научно-технической литературы. Большое внимание уделяется вопросам терминологии, что дает возможность увеличить активный словарь по специальности.
Методические указания предназначены для студентов специальности вычислительной техники и программного обеспечения, занимающихся техническим переводом.
Рецензент: доцент Серикбаева У. Б.
Печатается по плану издания некоммерческого акционерного общества «Алматинский университет энергетики и связи» на 2011 г.
© НАО «Алматинский университет энергетики и связи», 2011 г.
Сводный план 2011 г., поз. 293
Read and translate the text.
Some words from history of computers
Computers, as we know them today, have not been around for a long time. It was not until the mid-1940s that the first working digital computer was completed. But since then, computers have evolved tremendously. Vacuum tubes were used in the first – generation computers only to be replaced by transistors in the second-generation computers at the beginning of the early 1960s. By the end of the 1960s, transistors themselves were replaced by tiny integrated circuit boards and, consequently, a new generation of computers was on the market. Fourth- generation computers are now produced with circuits that are much smaller than before and can fit on a single chip. Even now, new technologies are being developed to make even better machines.
Exercise 1. Read the following paragraph and, as you read, underline the time relaters.
During the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, many easy ways of calculating were devised. Logarithm tables, calculus, and the basis for the modern slide rule were invented during this period. It was not until the early 1800s that the first calculating machine appeared and, not too long after, Charles Babbage designed a machine which became the basis for building today’s computers. A hundred year later, the first analog computer was built, but the first digital computer was not completed until 1944. Since then, computers have gone through four generations: digital computers using vacuum tubes in the 1950s, transistors in the early 1960s, integrated circuits in the mid – 60s, and a single chip in the 1970s. In the 1980s, we saw computers become smaller, faster, and cheaper. Earlier this decade, computers became portable, from laptops to palmtops. At the rate computer technology is growing now, we can expect further dramatic developments before the end of the end of the century.
Exercise 2. Read the following sentences which come from previous units. Underline the time relaters and indicate whether they refer to before, during, or after the given time reference. The first one has been done for you.
1. After Since then, over seventy million PCs made by IBM and other manufacturers have been sold.
2.
![]() Over this period, PCs have
become commodity items. Since IBM made the design non-proprietary, anyone can
make them.
Over this period, PCs have
become commodity items. Since IBM made the design non-proprietary, anyone can
make them.
3.
![]() Ten years later, in 1991, IBM were
making PCs with 16Mb of memory, expandable to 64 Mb, running with a processor
speed of a 33MHz.
Ten years later, in 1991, IBM were
making PCs with 16Mb of memory, expandable to 64 Mb, running with a processor
speed of a 33MHz.
4.
![]() Large companies are considering
running major applications on PCs, something which, ten years ago, no one would
have believed possible of a PC.
Large companies are considering
running major applications on PCs, something which, ten years ago, no one would
have believed possible of a PC.
5.
![]() When the computer finds the
closest match, it encodes the character in memory and displays it on the screen
as if it has been typed.
When the computer finds the
closest match, it encodes the character in memory and displays it on the screen
as if it has been typed.
6.
![]() Enter the clipboard computer, a
technology that has been in development for the last 20 years but took hold in
the mass market only this year.
Enter the clipboard computer, a
technology that has been in development for the last 20 years but took hold in
the mass market only this year.
7.
![]() Eventually, we’re all going to be
interlinked, no matter which service we use, in what DIALOG’s Richard Ream
calls a ‘network of networks’.
Eventually, we’re all going to be
interlinked, no matter which service we use, in what DIALOG’s Richard Ream
calls a ‘network of networks’.
8.
![]() Until then, most of us have to
go to more than one service to find everything we need.
Until then, most of us have to
go to more than one service to find everything we need.
Read and translate the text.
Computer networks
Computer networks link computers by communication lines and software protocols, allowing data to be exchanged rapidly and reliably. Traditionally, networks have been split between wide area networks (WANs) and local area networks (LANs). A WAN is a network connected over long- distance telephone lines, and a LAN is localized network usually in one building or a group of buildings close together. The distinction, however, is becoming blurred. It is now possible to connect up LANs remotely over telephone links so that they look as though they are a single LAN.
Originally, networks were used to provide terminal access to another computer and to transfer files between computers. Today, networks carry e-mail, provide access to public databases and bulletin boards, and are beginning to be used for distributed systems. Networks also allow users in one locality to share expensive resources, such as printers and disk systems.
Distributed computer systems are built using networked computers that co-operate to perform tasks. In this environment each part of the networked system does what it is best at. The high-quality bitmapped graphics screen of a personal computer or workstation provides a good user interface. The mainframe, on the other hand, can handle large numbers of queries and return the results to the users. In a distributed environment, a user might use his PC to make a query against a central database. The PC passes the query, written in a special language (e.g. Structured Query Language - SQL), to the mainframe, which then parses the query, returning to the user only the data requested. The user might then use his PC to draw graphs based on the data. By passing back to the user’s PC only the specific information requested, network traffic is reduced. If the whole file were transmitted, the PC would then have to perform the query itself, reducing the efficiency of both network and PC.
In the 1980s, at least 100,000 LANs were set up in laboratories and offices around the world. During the early part of this decade, synchronous orbit satellites lowered the price of long-distance telephone calls, enabling computer data and television signals to be distributed more cheaply around the world. Since then, fibre-optic cable has been installed on a large scale, enabling vast amounts of data to be transmitted at a very high speed using light signals.
The impact of fibre optics will be considerably to reduce the price of network access. Global communication and computer networks will become more and more a part of professional and personal lives as the price of microcomputers and network access drops. At the same time, distributed computer networks should improve our work environments and technical abilities.
Vocabulary:
blurred – become unclear or less distinct (затуманенный, неясный)
terminal – situated at the end (конечный, последний)
bitmap – a representation in which each item corresponds to one or more bits of information (битовый)
work station – a desktop computer terminal, more powerful than a personal computer (рабочая станция)
interface – a device or program enabling a user to communicate with a computer (интерфейс, взаимодействие)
mainframe – большая ЭВМ
query – a question, especially one expressing doubt or requesting information (усомниться)
parse – a program for parsing (делать разбор)
synchronous – existing or occurring at the same time (синхронный)
Exercise 1. Try to answer the questions.
1 What is a LAN?
2 What is a WAN?
3 What is distributed system?
Exercise 2. Match these words and phrases with their definitions
1. protocol a. analyze the syntax of a string of input symbols
2. bulletin board b. a teleconferencing system allowing users to read messages left by other users
3. user interface c. agreement governing the procedures used to exchange information between co-operating computers
4. make a query d. means of communication between a human user and a computer system
5. parse e. taking place at exactly the same time as something else
6. synchronous f. request a search
Exercise 3. Read this summary of the text and fill in the gaps using the list of words bellow.
Computer networks link computers by communication lines and software1_________ , allowing data to be exchanged rapidly and reliably. The2______, between local area and wide area networks is, however, becoming unclear. Networks are being used to perform increasingly diverse tasks, such as carrying e-mail, providing access to public databases, and for3 _____. Networks also allow users in one locality to share resources. Distributed systems are use networked computers. PCs or4 _______ provide the user5_______. Mainframe process6______ and return the results to the users. A user at his PC might make a query against a central database. The PC passes the query, written in a special language, to the mainframe, which then7 _______ the query, returning to the user only the data requested. This allows both the network and the individual PC to operate efficiently.
In the 1980s, at least 100,0008 ______were set up world-wide. As9______orbit satellites have lowered the price of long distance telephone calls, data can be transmitted more cheaply. In addition,10_______cable has been installed on a large scale, enabling vast amounts of data to be transmitted at a very high speed using light signals. This will considerably reduce the price of network access, making global networks more and more a part of our professional and personal lives. Networks should also improve our work11________and technical abilities.
distinction fibre-optic protocols synchronous
distributed systems LANs queries workstations
environments parses screen handling
Exercise 4. Look back in the text and find words that have a similar meaning to:
1 unclear a locality
2 place b global
3 carry out c to perform
4 cost d price
5 world-wide e blurred
Exercise 5. Now look back in the text and find words that have an opposite meaning to:
1 conflict v 1 enabling
2 preventing 2 reduce
3 tiny 3 vast
4 increase 4 co-operate
Programs and programming languages
Before reading the text, try to fill in the gaps in these sentences.
1. A _______ is a program written in one of the high- level languages.
2 .A program written in a high- level language must be interpreted into _______ before the computer will read and process it.
![]() 3 .A program designed to
perform a specific task is called an
3 .A program designed to
perform a specific task is called an
![]()
![]() 4. The or
is the program produced when the original program has
been converted into machine code.
4. The or
is the program produced when the original program has
been converted into machine code.
![]() 5. A
is a program that convert a high- level language into machine code.
5. A
is a program that convert a high- level language into machine code.
6. The systems program which fetches required systems routines and links them to the object module is known as the ______________________.
![]() 7. The is
the program directly executable by the computer.
7. The is
the program directly executable by the computer.
Now read the text to check your answers.
Computers can deal with different kinds of problems if they are given the right instructions for what to do. Instructions are first written in one of the high- level languages, e.g. FORTRAN, COBOL, ALGOL, PL/I, PASCAL, BASIC, or C, depending on the type of problem to be solved. A program written in one of these languages is often called a source program, and it cannot be directly processed by the computer until it has been compiled, which means interpreted into machine code. Usually a single instruction written in a high- level language, when transformed into machine code, results in several instructions. Here is a brief description of some of the many high- level languages:
FORTRAN acronym for FORmula TRANslation. This language is used for solving scientific and mathematical problems. It consists of algebraic formulae and English phrases. It was first introduced in the United States in 1954.
COBOL acronym for Common Business- Oriented Language. This language is used for commercial purposes. COBOL, which is written using English statements, deals with problems that do not involve a lot of mathematical calculations. It was first introduced in 1959.
ALGOL acronym for ALGOrithmic Language. Originally called IAL, which means International Algebraic Language. It is used for mathematical and scientific purposes. ALGOL was first introduced in Europe in 1960.
PL\I Programming Language I. Developed in 1964 to combine features of COBOL and ALGOL. Consequently, it is used for data processing as well as scientific applications.
BASIC acronym for Beginner’s All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. Developed in 1965 at Dartmouth College in the United States for use by students who require a simple language to begin programming.
C developed in the 1970s to support the UNIX operating system. C is a highly portable general-purpose language.
Other such languages are APL (developed in 1962), PASCAL (named after Blaise Pascal and developed in 1971), and LISP and PROLOG, both of which are used for work in artificial intelligence. LOGO is a development of LISP which has been used to develop computer-based training (CBT) packages.
When a program written in one of these high-level languages is designed to do a specific type of work such as calculate a company’s payroll or calculate the stress factor on a roof, it’s called an applications program. Institutions either purchase these programs as packages or commission their own programmers to write them to meet the specifications of the users.
The program produced after the source program has been converted into machine code is referred to as an object program or object module. This is done by computer program called compiler, which is unique for each computer. Consequently, a computer needs its own compiler for the various high-level languages if it is expected to accept programs written in those languages. For example, in order that an IBM RS/6000 may process a program in FORTRAN, it needs to have a compiler that would understand that particular model and the FORTRAN language as well.
The compiler is a systems program which may be written in any language, but the computer’s operating system is a true systems program which controls the central processing unit (CPU), the input, the output, and the secondary memory devices. Another systems program is the linkage editor, which fetches required systems routines and links them to the object module (the source program in machine code). The resulting program is then called the load module, which is the program directly executable by the computer. Although systems programs are the part of the software, they are usually provided by the manufacturer of the machine.
Unlike systems programs, software packages are sold by various vendors and not necessarily by the computer manufacturer. They are set of programs designed to perform certain applications which conform to the particular specifications of the user. Payroll is an example of such a package which allows the user to input data-hours worked, pay rates, special deductions, names of employees-and get salary calculations as output. These packages are coded in machine language (0s and 1s) on magnetic tapes or disks which can be purchased, leased, or rented by users who choose the package that most closely corresponds to their needs.
Vocabulary:
payroll - list of employees and the amount of money to be paid to each of them (платёжная ведомость)
acronym – a word formed from the initial letters of other words (аббревиатура)
consequently – as a result(следовательно)
artificial – made or produced by human beings rather than occurring naturally, especially, as a copy of something natural(искусственный)
purchase – buy(покупать)
commission – order or authorize ( a person or organization) to do or produce something(поругать)
convert – change the form, character, or function of something(превращать)
refer – mention(упоминать, ссылаться)
compile – produce(a list or book) by assembling information collected from other sources(собирать)
accept – consent to receive(принимать)
link – make a connection with or between(соединять)
fetch – go for and then bring back(приносить)
executable – (of a file or program) able to be run by a computer
vendor – a person or company, offering something for sale(продавец)
conform – comply with rules or standards(подчиняться)
Exercise 1. These answers to questions about the text. Write the questions.
1. No, it is quite wordy so it is used for commercial purposes.
2. To support the UNIX operating system.
3. An applications program.
4. It is done by compiler.
5. It fetches required systems routines and links them to the object module.
6. No, they are also sold by other vendors.
Exercise 2. Summarize the information on different high-level computer languages by completing the table below.
|
Language |
Developed |
Function |
Characteristic |
|
FORTRAN |
|
|
|
|
|
1959 |
|
|
|
|
|
mathematical and scientific purposes |
|
|
|
|
|
combines features of COBOL and ALGOL |
|
BASIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
to support UNIX operating system |
|
|
|
1962 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise 3. Find the passages in the text where the following ideas are expressed.
1. Systems programs control the work of the computer system.
2. Software packages are not always sold by manufacturer.
3. Usually, every high-level instruction translates into many more in machine code.
4. Systems programs are usually provided by the manufacturer.
5. Programmers may be required to write software for their employers.
Exercise 4. Find words that have a similar meaning.
1. Converted a. corresponds
2. Give the responsibility to b. transformed
3. Brings c. commission
4. Are compatible with d. fetches
5. Matches e. conform to
Exercise 5.Choose the correct word to complete each sentence. You have to change some words slightly.
1. Instruction, instruct, instructed, instructor.
a) Our maths _______________explained to us the principles of binary arithmetic.
b) We were _____________to document our programs very carefully.
c) Both _______________and data have to be changed to machine code before the computer can operate on them.
2. Compilation, compiler, compile, compiled
a) Our university computer does not have a PASCAL_____________.
b) Usually, a programmer _____________his program before he puts in the data.
c) A source program cannot be directly processed by computer until it has been__________.
3. Result, results, resulting
a) The linkage editor links system routines to object module. The _____________program, referred to as the load module, is directly executable by the computer.
b) The ____________________of these mathematical operations were obtained from the university mainframe and not from my micro.
4. Specification, specify, specific, specified, specifically.
a) Our company bought three packages with very ______________applications: payroll, accounts receivable, and account payable.
b) An application is designed to do a___________ type of work, such as calculating the stress factor of a roof.
c) Did the analyst give the new programmer the ______________necessary to start on the project?
Read the program below.
/* CALCULATE AVERAGES */
main()
{ float a, b, c, d, average;
printf(“Enter three numbers:”);
scanf(“%f %f %f”,&a, &b, &c);
d=a+b+c;
average=d/3.0;
printf(“the average is %f”,average); }
Read and translate the text.
Comment lines
A C source program consists of statements and comment lines. Comment lines are enclosed by the characters /* (at the start of the comment) and */ (at the end of the comment)
The function main{}
Every C program must have a function called main which must appear only once in program. The parentheses following the word main must be present, but there must be no parameters included. The main part of the program is enclosed within braces {}, and consists of declaration statements, and other C functions. In the above program there are six statements within the braces: a declaration statement (the first statement of the main program starting with the word float), two assignment statements (the fourth and fifth statements starting with the variable names d and average) , and three function statements, two to print information on the screen and one to scan the keyboard for input.
As C is a free form language, the semicolon (;) at the end of each line is a must. It acts as statement terminator, telling the compiler where an instruction ends. Free form means that statements can be identified and blank lines inserted in the source file to improve readability, and statements can span several lines. However, each statement must be terminated with a semicolon. If you forget to include the semicolon, the compiler will produce an error, indicating the next line as the source of the error. This can cause some confusion, as the statement objected to can be correct, yet as a syntax error is produced.
Variables and the Declaration Statement
A variable is a quantity that is referred to by name, such as a, b, c, d, and average in the above program. A variable can take on my values during program execution, but you must make sure that they are given an initial value, as C does not do so automatically. However, before variables can be used in a program, they must `be declared in a type declaration statement.
Vocabulary :
comment - express an opinion or reaction in speech or writing
( комментарий)
character - a printed or written letter or symbol (буква, литера, знак)
parentheses - a pair of round brackets ( ) used to include such a word or
phrase ( круглые скобки)
braces – (скобки)
terminate – bring to an end (завершать)
blank – empty (пустой )
insert – include (включить, вставить)
span – extend (расширяться)
confusion – mistake (ошибка)
object – disapprove (возражать)
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences.
1. The Function______________must appear only once in program.
2. /*CALCULATE AVERAGES*/ is a________________line.
3. The statement float a,b,c,d,average; is a_______________statement .
4. The program below contains______________function statements.
5. The assignment states are on lines___________and_________________.
6. The main part of the program is enclosed within______________.
7. Each line of any C program must end with a___________, which acts as a statement______________.
8. If you forget to include the correct punctuation, the___________will produce a__________error.
9. A quantity referred to by name is known as a__________.
10. A________________ _________________statement must be used to declare variables.
Exercise 2. Match each word with the correct definition.
1) brackets a) float
2) not fixed b) parentheses
3) recognized c) identified
4) completed d) terminated
Exercise 3. The table below shows C’s relational operators. Fill the gaps in the table.
|
C symbol |
Meaning |
|
= = |
еqual to |
|
< |
1___________ |
|
2_______________ |
equal to or less than |
|
> |
3_____________ |
|
>= |
4_____________ |
|
!= |
5_____________ |
Before reading the text, match these words with their definitions:
a) clipboard 1) surface on which pictures or data are shown
b) stylus 2) electrical force
c) screen 3) pattern use as a guide for creating letters or characters
d) grid 4) individual dot on a computer screen
e) voltage 5) network of lines crossing at right angles
f) pixel 6) pointed implement for drawing or writing
g) template 7) portable board with a clip at the top for holding papers
Read the text and decide why the author chose the title Delete keys. Can you suggest a better title.
Delete Keys – Clipboard Technology
For the last generation, Silicon Valley and Tokyo have been working to design computers that are ever easier to use. There is one thing, however, that has prevented the machines from becoming their user-friendliest: you still have to input data with a keyboard, and that can require you to do a lot of typing and to memorize a lot of elaborate commands.
Enter the clipboard computer, a technology that has been in development for the last 20 years but took hold in the mass market only in this year. Clipboard PCs – which, as their suggests, are not much bigger than an actual clipboard – replace the keyboard with a liquid crystal display (LCD) screen and an electronic stylus. Users input data by printing individual letters directly on the screen.
There are two technologies at work in clipboard PC: one allows raw data to get into the computer and the other allows the computer to figure out what that means. The first technology relies principally on hardware and varies depending on the particular computer. In one system, marketed under the name GRIDPad, the computer’s LCD screen is covered by a sheet of glass with a transparent conductive coating. Voltage is sent across the glass in horizontal and vertical lines forming a fine grid: at any point on the grid, the voltage is slightly different. When the stylus – which is essentially a voltmeter – touches the screen, it informs the computer of the voltage at the point. The computer uses this information to determine where the stylus is and causes a liquid crystal pixel to appear at those coordinates. The position of the stylus is monitored several hundred times a second, so as the stylus moves across the glass, whole strings of pixels are activated.
“What we do is sort of connect the dots”, says Jeff Hawkins, the creator of GRIDPad. “Users can then write whatever they want on the screen with a kind of electronic ink”. Marking that writing comprehensible to the computer, however, requires the help of some powerful software. When the stylus is being used, the computer is programmed to look for moments when the tip does not touch the screen for a third of a second or more. Every time this happens – and it happens a lot when somebody is printing – the software assumes that one letter or number has been written. The pixel positions of this fresh character are then passed on to the computer’s pattern recognition software, which instantly identifies the letter or number written.
The software does this by first cleaning up the character – smoothing out crooked lines and removing errant dots. The remaining lines and curves are then compared with a series templates in the computer’s memory that represent hundreds of thousands of different versions of every letter in the English alphabet and all ten numerals. When the computer finds the closest match, it encodes the character in memory and displays it on the screen as if it had been typed. The entire process takes just a fraction of a second. To delete a word, you simply draw a line through it. To move to the next page, you flick the stylus at the bottom of the screen as if you’re flicking the page of a book.
There a handful of clipboard computers now on the market, including GRIDPad, which is sold in the US; Penvision, manufactured by NCR and sold around the world: and Sony’s Palmtop and Canon’s Al Note, both sold only in Japan. IBM and Apple are also pouring millions dollars into the technology.
In addition to this hardware, a variety of software is also making its way to the market. Depending on the power of the computer and the sophistication of the software, clipboard systems can be programmed to understand the particular quirks of a particular user’s printing; this is an especially useful feature in Japan, where elaborate kanji characters make up most of the written language. Improvements in software may soon allow machines sold in the US to understand not only printing but continuous script as well.
Given such flexibility, the designers of clipboard computers are predicting big things – and a big market – for their products. “There’s no doubt about it”, says an optimistic Hawkins. “You’re going to own one of these things in the not-too-distant future”.
Vocabulary:
printing – (in this case) writing separated letters or numbers by hand
kanji – Japanese script which uses Chinese characters
clipboard – a temporary storage area where material cut or copied from a file is kept before being pasted into another file
elaborate – detailed and complicated in design and planning(сложный)
raw data – not analysed, evaluated or processed for use
grid - (решётка)
comprehensible – able to be understood, intelligible (понятный)
crooked – bent or twisted out of shape or out of place(согнутый)
errant - mistaken
template – a preset format for a document or file
flick - turn
handful – a small number or amount
quirk – a sudden twist, turn or curve
Exercise 1. Decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F) in relation to the information in the text. If you think a statement is false, change it to make it true.
1. The Americans and Japanese are working together to produce user-friendlier computers.
2. The clipboard computer was first sold twenty years ago.
3. On a clipboard, an electronic pen replaces the traditional keyboard.
4. In the GRIDPad system, when the pen touches screen, it informs the computer and a liquid crystal pixel appears at that point.
5. The software decides that one character or number is complete if the tip of the stylus is not in contact with the screen for more than half a second.
6. The whole process of recognizing letters or numbers and printing them on the screen takes very little time.
7. There are many clipboard computers sold today which are all available everywhere in the world.
8. Clipboard systems can be made to understand any kind of writing.
Exercise 2. Use the information in the text to complete the dialogue in your own words.
A. How big is a clipboard PC?
B.
A. Does it have a keyboard?
B.
A. How does the stylus work?
B.
A. How does the computer know when one letter or number is complete?
B.
A. And how does the computer recognize different letters?
B.
A. Can you delete a word after you have written it?
B. Yes.
A. Are these systems capable of recognizing joined writing?
Exercise 3. Find words that have a similar meaning to
1. Understand a. marketed
2. sold b. to figure out
3. covering c. coating
4. points d. connect
5. join e. coordinates
6. making even f. crooked
7. not straight g. smoothing out
8. made by mistake h. flick
9. move quickly and sharply i. errant
10. unique features j. quirks
Exercise 4. Choose the correct word to complete each sentence. You may have to change some words slightly.
1. Electron, electronic, electronics, electronically.
a. An _____________ pen is one example of an input device.
b. A computer solves problems___________.
c. Many _____________ students go on to work as engineers.
2. Technology, technologist, technological, technologically.
a. The computer is the greatest _______________ invention of the twentieth century.
b. There are two ____________ involved a clipboard PC.
c. Today’s computers are ___________ the superior to those used a few years ago.
3. Identify, identifying, identifiable, identity.
a. The clipboard’s pattern recognition software immediately__________ the letters and numbers written by the stylus.
b. Most computer companies will not allow people without an ___________ card to enter their premises.
c. A password is a mechanism for ____________ the computer-user and allowing access.
4. Compute, computing, computation, computerize, computerization.
a. The _____________ of the manufacturing division will be expensive in the short term, but cost-effective in the long term.
b. We should able to ___________________ our profit for next year fairly accurately with the new program.
c. I could tell from all the ______________ on the board that a maths lesson was in progress.
Exercise 5. Discuss the following questions:
1. What are the limitations of portable computers?
2. Do you think students should be allowed to use portable computers in class?
Before reading the text, try to decide which of the following definitions best describes a management information system:
a. a system for supplying information to management
b. a system for managing information
c. a system which supplies information about management
Exercise 1. Decide whether these statements are true (T) or false (F), then read the text to check your answers.
1. All businesses are interested in more or less the same information, regardless of the nature of their operations.
2. The managing director of a company needs a lot of more detailed information about the day-to-day operations than his executives do.
3. Functional management requires up-to-the-minute information so that they can take action to control events as they happen.
4. Information systems are usually computerized.
5. Transaction processing systems are usually the first systems to be installed.
Information systems
The objective of information systems is to provide information to all levels of management at the most relevant time at an acceptable level of accuracy, and at an economical cost.
Individual businesses require information according to the nature of their operations. A car manufacturer is particularly interested in the extent of competition from overseas manufacturers in the home market and competition from other home-based manufacturers. A tour operator is concerned about purchasing power and its effect on holiday bookings and the political situation prevailing in the various countries.
As a general guide, the detail contained in reports containing information varies according to the position of the recipient in the hierarchical management structure. The chairman and managing director of a company require details of operations which are broad in scope and which concentrate key factors pinpointing economic and financial trends. Functional management require information relating to relating to the departments they are responsible for in sufficient detail to enable them to apply whatever measures are required to bring situations into line with requirements. They require information relating to events as they occur so that appropriate action can be taken to control them. Information systems are often computerized because of the need to respond quickly and flexibly to queries. At the bottom level in the information hierarchy are the transactions processing systems, which capture and process internal information, such as sales, production, and stock data. These produce the working documents of the business, such as invoices and statements. Typically, these are the first systems which a company will install. Above the transaction-level systems are the decision support systems. These take external information – market trends and other external financial data – and processed internal information, such as sales trends, to produce strategic plans, forecasts, and budgets. Often such systems are put together with PC spreadsheets and other unconnected tools. Management information systems lie at the top of the hierarchy of information needs. The MIS takes the plans and information from the transaction-level systems to monitor the performance of the business as a whole. This provides feedback to aid strategic planning, forecasting, and/or budgeting, which in turn affects what happens at the transactional level.
Vocabulary:
objective – a thing aimed at or sought; a goal(цель)
relevant – closely connected or appropriate to the matter in hand(относящийся к делу, уместный)
extent – the particular degree to which something is or is believed to be the case(степень, диапазон)
concerned – worried, troubled or anxious (заинтересован, обеспокоен)
purchase – acquire (something) by paying for it ; buy (покупать)
booking – an act of reserving accommodation a ticket, etc in advance(заказ)
recipient – a person or thing that receives or is awarded something(получатель)
in scope – (размах, охват)
pinpoint – find or identify with great accuracy or precision
query – a question, especially one expressing doubt or requesting information(вопрос)
capture – record accurately in words or pictures(захватывать)
invoice – a list of goods sent or services provided, with a statement of the sum due for these(счёт-фактура)
install – place or fix in position ready for use(устанавливать)
Exercise 1. Draw a diagram to show how information systems, as described in the last paragraph. Your diagram should show the hierarchy of systems and should include examples of the kind of information involved at each stage in the process. Use arrows(→) to indicate the flow of information.
Exercise 2. Complete the puzzle and find the key word in 10 down.
Across
1. The ‘I’ of MIS. (11)
2. Another term for VDU. (7)
3. See 8.
4. An A/D _____ changes analog signals into digital signals. (9)
5. The ‘D’ of VDU.(7)
6. The decision _____ systems combine information from outside and inside and organization to produce strategic plans and forecasts.
7. Voice _____ systems permit people to talk to computers. (11)
8. and 3_____ _____ systems capture and process information generated within an organization (e.g. sales and production data). (11,10)
9. Converted from an analog digital signal. (9)
Down
The amount of deskspace (or floorspace) taken up by a computer. (9)
Using the diagram below, complete the following paragraph.
A Computer system
A computer, has basic components: input, processor, memory and output. The CPU consists of two parts: the _____________, which directs and controls the signals and commands inside the processor, and the _____________ unit, which does the arithmetic operations and the decision-making operations. While the ______________ is made up of a _____________, a _____________, a ______________, and a ______________, the ______________ is composed of ______________, a ______________, and ______________.
In a computer, internal memory or ______________ refers to the storage locations inside the computer, whereas ______________ refers to the storage embodied in the peripherals. _____________ may be divided into _____________ (_____________) and ______________ (_____________). The ______________ devices can be either a _____________, a _____________, or a ______________,
These devices enter information the computer . After the processor has operated on it, the ____________devices display the results of the computations on either a ____________or a ____________,or store them on tape or disk for future use.
A Computer system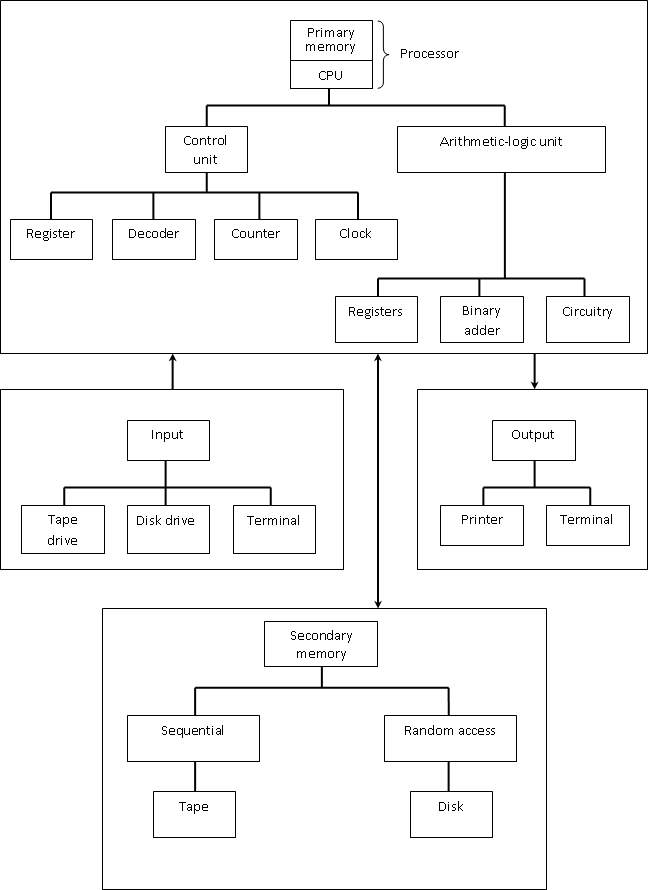
Listing
It is important when reading to recognize and understand the relationship in which sentences and groups of sentences combine to present information. This information may be linked by means of a connective word or marker.
Making a list, for example when enumerating, and giving instructions, indicates a cataloguing of what is being said. It is important to note that most enumerations belong to clearly defined sets. The following table is a list of the markers that can be used to show the order in which things are to be said.
1, 2, 3, etc.
one, two, three, etc.
first(ly), second(ly), third place
another, next, then
furthermore, afterwards, moreover
lastly/finally
to begin/start with, and to conclude
![]() first and
foremost mark the beginning
first and
foremost mark the beginning
first and most important(ly) of a descending order
![]() above all mark
the end of
above all mark
the end of
last but not least an ascending order
There are many ways of showing sequential relationships. Those given in the table above are not the only ones, they are the most common ones used in listing or enumerating. The-ly forms are usually used when listing.
Sample paragraph:
More and more police departments are now using sophisticated devices to help control the increasing crime rate. Some of these devices are: firstly, a computer terminal inside a police vehicle to answer an officer’s questions, secondly , a computer-controlled display unit for displaying fingerprints, and thirdly, educational systems for police officers such as terminals, enabling them to verify changed in laws, rules, and regulations.
The computer memory of many law enforcement systems contains all kinds of information. First and foremost, it has data on stolen items such as cars, licence plates, and property. Second, it has information on missing persons and wanted fugitives. Last but not least, it contains information on political extremist groups and their activities.
Computers have certainly revolutionized police work by providing access to millions of items of information with the least possible delay and speeding up the process of apprehending suspicious-looking characters.
Exercise 1. Complete the following paragraph about the various steps in the creation of a database by filling in the blanks with appropriate listing markers.
When you are creating a new database, you must1 _________ decide how many fields you will need in your database.2 __________, you will have to provide up to five items of information about each field.3 _________,each field needs to have a name.4 _________, the field type has to be defined. Character, numeric, date, and logical are some common types.5 __________ choice to be made is the width of the field. However, some fields, such as date, have present default values. The6 _________ step is to set the number of decimal places if the field is numeric.7 __________, you will have to indicate whether the field is to be indexed or not.
Exercise 2. Complete the following paragraph by filling in the blanks with appropriate listing markers.
Computers can do wonders, but they can waste a lot of money unless careful consideration goes into buying them. Businessmen and women thinking of buying a computer system should 1 ____________ admit they know very little about computers.2___________, they must realize that the computer sales people don’t always know how their business works.
3 _________, it is essential that buyers should get outside advice, not necessarily from consultants but from other executives who have had recent experience in buying a computer system.4 ___________they should try to see systems similar to ones under consideration in operation. Because their operations will have differences that must be accommodated, they should 5_________ find out what would be involved in upgrading a system. 6 __________ important thing to know before buying a computer is the financial situation of the supplier because computer companies come and go and not all are financially stable.7 __________,the prospective buyer should demand that every detail be covered in writing, including hardware and software if they are supplied by different companies. There’s nothing wrong with computers themselves, it’s how and why they are used that can cause problems.
Read and translate the text.
How they work
Although the computer screen has the standard characteristics of a TV display, images are produced in a very different way. If you want to record anything from your computer to video for play-back on a TV monitor, you need a print-to-tape device.
In a TV display, a tight beam of electrons scans the screen in much the same way you read a page of text-from the upper-left corner, it moves line by line to the lower right. Usually, one pass writes the entire image once. The number of passes the beam writes per second is called the beam writes per second is called the vertical refresh rate and is measured in kilohertz. Most computer systems follow the American TV standard and use a vertical refresh rate of 60kHz whereas PAL, the European TV standard, requires 50kHz.
Another difference is with bandwidth. When PAL was defined, the bandwidth available for a TV signal was very narrow. While the TV image had to be refreshed at least 50 times a second for flicker to remain unnoticeable, there was not enough bandwidth to transmit all 625 lines of one TV image in a fiftieth of a second. The developers of PAL, therefore, employed a clever trick called interlaced video. They split each frame of the image into two fields of 312.5 lines, the odd lines into field A, the even ones into field B. The fields are transmitted at a rate of 50 per second, leaving us with an effective frame rate of 25 per second while eliminating most of the flicker.
This is fine for viewing from several yards, but should you move as close to your TV as you would to your computer screen, you’d end up with a headache after half an hour. Also, if any parts of the displayed image occupy only one horizontal scan line, that scan line will flicker quite noticeably at 25kHz.
All video equipment works with PAL-standard, 50kHz interlaced video. Computers tend to use 60kHz (or more), non-interlaced video and look more stable. To get a signal from your computer to record on a VCR, there are two possibilities:
1) Use a display adaptor that can produce PAL-standard video. You would not be able to connect such a card to a standard computer monitor, however. A video monitor or a multi-sync monitor is needed. You wouldn’t want to look at such a screen for hours on end – interlaced video is not suitable for word processing.
2) Put up with the standard display signal from your computer (probably 60kHz) and use a scan converter. It can take a video signal with one refresh or scan rate, and convert it to the other. A scan rate, and converter is actually a small digital frame-grabber with asynchronous video output.
Vocabulary:
yard – measure of length(1 yard = 0.914m)
play-back - (воспроизведение)
pass-transfer-(пас, передача)
refresh-give new strength or energy to-(освежать)
rate-the speed with which something moves or happens-(скорость)
bandwidth-a range of frequencies within a given band, in particular that used for transmitting a signal
flicker-fluctuations in the brightness of a film or television image such as occur when the number of frames per second is too small for persistence of vision-(мерцание)
interlace- scan (a video image) in such a way that alternate lines form one sequence which is followed by the other lines in a second sequence.
odd -(нечетный)
even -(четный)
stable - firmly established (столичный)
sync - synchronization
convert - be able to change from one form to another
asynchronous –controlling the timing of operations by the use of pulses sent when the previous operation is completed rather than at regular intervals
Exercise 1. Match the sentence halves to form complete sentences.
1. If you want to play back anything from your computer on a TV monitor.
2. If you computer system follows the American TV standard.
3. If you use a monitor with interlaced video for word processing .
4. If you use a display adaptor that can produce PAL-standard video.
5. If you want to use the standard display signal from your computer.
a. it will have a vertical refresh rate of 60kHz.
b. you must use a scan converter.
c. you need a print-to-tape device.
d. you cannot use a standard computer monitor, but must use a video or multi-sync monitor instead.
e. you will get a headache!
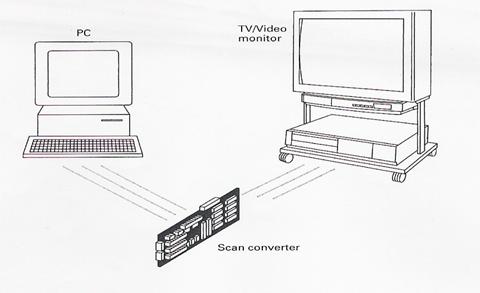
Exercise 2. Which of the two configurations for computer-to-video conversation suggested in the text does this diagram show?
Word-play
Exercise 3. Find the hidden words in this square. Some appear vertically, some horizontally, and some diagonally. They may be upside-down or back to front. Use the clues on the opposite page to help you. The number of letters in each word and the first letter of the word appear in brackets after the clue.
N O N E M O N E H P E
E A D A P T O R E M S
N T R O U B E S O U L
O A C C E P L E P R O
H E S P A N D E T A T
P E C I F I R C A T I
O M R F E V O B N U O
R A F L I C K E R O N
C L E S C A N T R I S
I C O M P O U N D N G
M R N O I T A M I N A
Find words which mean:
1) A strange thing or event. (10, P)
2) An instrument that changes soundwaves into electrical current. (10, M)
3) A display ________ is one device used in computer-to-video conversation. (7,A)
4) Mend. (6, R)
5) A person who monitors the way people work to check that things are done properly. (10, S)
6) An opening on a computer into which fits an expansion board. (4, S)
7) To shine unsteadily. (7, F)
8) A _______ document is made up of two or more documents combined together. (8, C)
9) A _______ converter is another device used in computer-to-video conversation. (4, S)
10) The technique whereby still drawings are given the appearance of movement. (9, A)
Exercise 1. Can you explain what these abbreviations mean?
1 ROM
2 RAM
3 CPU
4 I/O
Check your answers by reading quickly through this text:
Microcomputers systems
The block diagram of a microcomputer system is shown in Fig. 1.
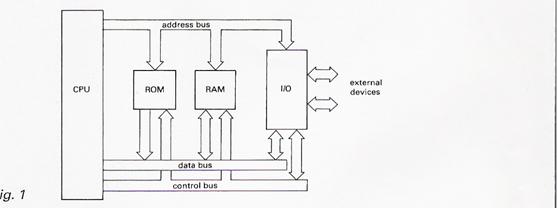
Fig. 1
The I/O (input/output) unit consists of one or more ICs, which are used to control the data going in and out of the computer.
The ROM (read-only memory ) and RAM (random-access memory) units consist of a number of special digital logic chips which can store programs and data. The small ROM provides some permanent storage and the RAM is used for temporary storage. Unlike the ROM, the contents of the RAM is constantly changing, but it only operates while the computer is switched on.
The CPU (central processing unit) is a microprocessor. It is the main part of the computer, which controls the rest of the system and performs all the arithmetic and logic operations on the data.
Sets of connectors known as buses are used to carry the internal signals between each unit. The data bus is used to transfer data between all the units. The control bus is used to send control signals from the CPU to the other units. The control bus is used to send control signals from the CPU to the other units. The address bus is used to send signals from the CPU which indicate the memory and I/O locations to be used.
Exercise 2. Fill in the gaps in this table with the help of the text.
|
Component |
Purpose |
|
I/O unit |
controls data going in and out of the computer |
|
ROM |
|
|
|
temporary storage |
|
|
controls the system, performs all arithmetic and logic operations on the data |
|
Data bus |
|
|
Control bus |
|
|
|
sends signals from the CPU which indicate the memory and I/O locations to be used |
Study these ways of describing the purpose of random access memory:
RAM is used for the temporary storage of programs and data.
RAM is used for storing programs and data temporarily.
RAM is used to store programs and data temporarily.
Exercise 3. Identify each of the electronic components or pieces of equipment described below. Compare answers with your partner.
1 It’s used to change AC voltage from small to large or from large to small.
2 It’s used for measuring very small currents.
3 It’s used to check the logic levels in the pins of ICS.
4 It’s used as part of a burglar alarm to detect movement.
5 It’s used for the transmission of RF signals.
6 It’s used for protecting circuits from a surge in voltage.
7 It’s used to master down different recordings to make a master tape.
8 It’s used to find buried metal.
Exercise 4. Look again at the sentences describing the purpose of RAM. Describe the purpose of each of the other components listed in your completed table in Task 2.
Study this term from electronics:
semiconductor
We can divide it into three parts:
semi conduct or
Semi is a prefix which means ‘half’, while or is a suffix added to the verb conduct to make a noun. From this we can work out that a semiconductor is a component which half conducts, i.e. it conducts in one direction only.
Knowledge of common prefixes can help us to work out the meaning of some unfamiliar terms in electronics.
Exercise 5. Study this table. Try to think of other examples to add. Compare your examples with those of another group.
Explain to the other group the meaning of any terms which they are unfamiliar with.
|
Prefix |
Meaning |
Example |
Others |
|
de- |
reverse the action |
decouple |
|
|
dis- |
opposite of |
discharge |
|
|
micro- |
small |
microchip |
|
|
multi- |
many |
multimedia |
|
|
tele- |
Far |
television |
|
|
trans- |
across |
transmitter |
|
Technical reading
Combinational logic
Exercise 1. Answer the following questions about the text below.
1 What terms are used in the text for each of the following?
a a digital switching circuit
b the output of each gate depending on the combination of its inputs
c the number of ICs used in a computer
d an indication of the number of components used in an IC
2 What is shown by
a a truth table?
b a pin-out diagram?
3 What is another name for a NOT gate?
4 What are the two common families of logic ICs?
5 What do these abbreviations stand for?
a TTL
b VLSI
c CMOS
d MSI
6 Which of these statements are true for CMOS ICs?
a They contain bipolar transistors
b They contain field effect transistors
c They are particularly suitable for use in battery-operated portable computers
d They are particularly suitable for use in large, high-speed computers
The decision-making circuits used in modern computers are mainly composed of combinations of digital switching circuits known as logic gates. Fig.1 shows the logic symbols and truth tables for some basic gates.
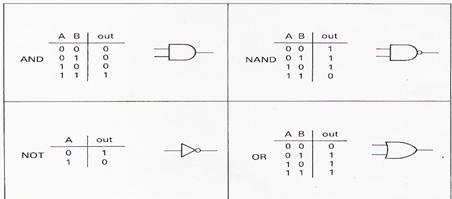
Fig.1
The output of each gate depends on the combination of its inputs. This is known as combinational logic. The output for all possible inputs is shown using a truth table. The truth tables show that the output of an AND gate is only high (i.e.logic level 1) when all its inputs are high. The output of a NAND gate, however, stays high unless all its inputs are high. The output of a NOT gate (also known as an inverter) is always the opposite of its input.
Computers use ICs which contain a number of logic gates on one chip. An IC pin-out diagram shows the arrangement of the gates and the function of each pin on the chip (see Fig.2).
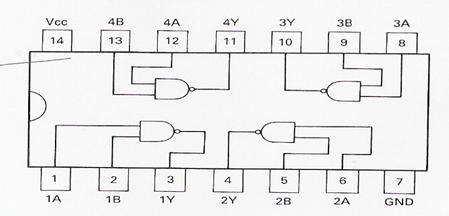
quad 2 input NAND gates
TTL 7400 (CMOS 4011)
Fig.2
The number of ICs used in a computer, i.e. the chip count, can be reduced by connecting NAND gates together to form other types of gates (see Fig.3)
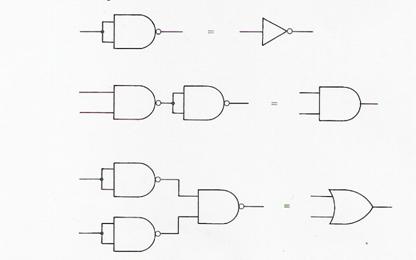
How NAND gates can be used to make basic logic gates
Fig.3
The number of components in an ICs is indicated by its scale of integration as shown in Table 1. The IC shown in Fig.2 is an SSI device but microprocessors used in computers are VLSI or SLSI devices.
Table 1
|
Scale of integration |
Abbreviation |
No. of active components |
|
Small-scale integration |
SSI |
1 to 10 |
|
Medium-scale integration |
MSI |
10 to 102 |
|
Large-scale integration |
LSI |
102 to 103 |
|
Very large-scale integration |
VLSI |
103 to 104 |
|
Super large-scale integration |
SLSI |
104 to 105 |
The are two common families of logic ICs used in computers. TTL (transistor-transistor logic) ICs use bipolar transistors to form each gate whereas CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) ICs use field effect transistors (FETs). The different characteristics of each family determine which will be used in a particular computer (see Table 2.) For example, TTL ICs are used in large, high-speed computers and CMOS ICs are better for battery-powered portable computers.
Table 2
|
Properties |
TTL |
CMOS |
|
Supply voltage |
+5V±0.25% |
+3V to +15V |
|
Supply current |
mA |
µA |
|
Power dissipation |
mW |
µW |
|
Switching speed |
Fast |
relatively slow |
|
Input impedance |
low |
high |
Exercise 2. Complete these statements with the help of the truth tables in Fig.1. For example in the case of an AND gate:
a When A and B are low, the output is low.
a When A is low and B is high, the output is low.
1 AND When A is high and B is low, __________________.
2 NOT _______________________, the output is high.
3 OR When A and B are high, ________________________.
4 NOT When A is high, ____________________________.
5 NAND ______________________, the output is low.
6 NAND When A is high and B is low, ________________.
7 AND ________________, the output is high.
8 NAND When A and B are low, ______________________.
Exercise 3. Study this diagram. It shows an industrial process is controlled using logic gates. With the help of the diagram, complete the blanks in the explanation which follows. Each blank may be one or more words.
A motor controlling the flow of aluminium blanks to a hydraulic press is switched on only under these conditions:
1. The power is on.
2. The supply voltage is1 _______________.
3. There are2 _______________ aluminium blanks in the hopper (store).
4. The3 ________________in the hydraulic press is correct.
Information on these four conditions is fed into an4 ____________as all four conditions must be satisfied for the motor to run. When5 __________, the output from the AND gate is high. This is fed into the store input of the 6 _________unit to provide a continuous signal to operate the motor.
The motor must stop if any one of these conditions occurs:
1. The power is7 ________.
2. The8 _________ rises.
3. The hopper is9 ________.
4. The10 ________drops.
Information on each of these conditions is fed through a11_________. When the input is low12,__________. The output from each NOT gate is fed to an13 ______. When any of the four inputs to the OR gate is high, the output14_______. When this is fed to the memory reset, it interrupts the continuous signal to the motor. The motor is switched15_________ and the flow of aluminium blanks to the press is thus16_________.
Список литературы
1. P. Charles Brown and Norma D.Mullen. English for Computer Science, Copyright, Oxford - 1992
2. Steven H.Kim. Designing Intelligence: A Framework for smart systems, Copyright, Oxford - 1991
3. C.A.Немногин. Turbo Pascal. Санкт-Петербург - 2001
4. Г.А.Сырецкий. «Информатика.» Фундаментальный курс. Том1. Основы информационной и вычислительной техники. Санкт-Петербург - 2005
5. H.W.Brimicombe. Introducing Electronic Systems. Thomas Nelson and Son LTD - 1987.
Содержание
|
Some words from history of computers |
3 |
|
Computer networks |
4 |
|
Programs and programming languages |
6 |
|
Comment lines. The function main |
11 |
|
Variables and the Declaration Statement |
12 |
|
Delete Keys – Clipboard Technology |
13 |
|
Information systems |
18 |
|
A computer system |
21 |
|
Listing |
23 |
|
How they work |
24 |
|
Microcomputers systems |
28 |
|
Technical reading |
31 |