Некоммерческое акционерное общество
АЛМАТИНСКИЙ ИНСТИТУТ ЭНЕРГЕТИКИ И СВЯЗИ
Кафедра Иностранные языки
Английский язык
Методические указания для развития перцептивных умений
для студентов 1 курса всех специальностей
Алматы 2010
СОСТАВИТЕЛЬ: Сергеева Л.Д. Английский язык. Методические указания для развития перцептивных умений для студентов 1 курса всех форм бучения всех специальностей. – Алматы. АИЭС, 2010. – 34 с.
Методические указания предназначены для развития перцептивных умений технических текстов на основе учебника Орловской И.В. и предназначены для студентов 1 курса всех специальностей. Целью методической разработки является формирование у будущих инженеров перцептивной и когнитивной компетенций. Применение коротких видеоматериалов, продолжительностью 3-5 минут способствует более полному восприятию информации в сфере новейших технических разработок. При просмотре видео материалов происходит соединение зрительного образа со слуховым, новая лексика воспринимается в полном объеме, происходит детальное понимание звучащего текста. Методические указания рекомендуются к изданию.
Методические указания предназначены для развития перцептивных умений технических текстов на основе учебника Орловской И.В. и предназначены для студентов 1 курса всех специальностей. Целью методической разработки является формирование у будущих инженеров перцептивной и когнитивной компетенций. Применение коротких видеоматериалов, продолжительностью 3-5 минут способствует более полному восприятию информации в сфере новейших технических разработок, так как при просмотре видео материалов происходит соединение зрительного образа со слуховым, новая лексика воспринимается в полном объеме, происходит детальное понимание звучащего текста. Методические указания рекомендуются к изданию.
Unit 1
Education
Video 1
“Tales from America”
A film by Daniel Emmerson
Pre – watching
Activity 1
How much do you know about America? Test yourself with this “true or false” quiz!
1. America is the largest country in the world.
2. New York is the capital city of the USA.
3. New York was originally called New Amsterdam.
4. The USA celebrates its independence from Birthday on 4th July every year.
5. There are 51 states in the USA.
6. The first US President was Lincoln.
Watching
Activity 2
Now watch the first part of the film about learning English in the USA. As you watch, fill in the table below.
|
Interviewee |
Nationality |
Occupation |
Why is she/he in the USA? |
|
Lee Nitel |
|
Student |
For a university course she will start next month in her own country. |
|
Aneta Kaint |
Australian |
Student |
|
|
A Rum Yang |
|
Student |
To feel closer to native speakers. |
|
Adrian Petrov |
Argentinian |
Engineer |
|
Activity 3
Now watch the rest of the film. The interviewees in the film answer the following questions. Read the questions below and discuss what you think the interviewees might say in response. Then watch the video once to find out if your ideas were right.
1. Why do learners visiting New York think studying English is important?
2. What problems do people have when learning English?
3. How does being in New York help with these problems?
4. What tips do learners visiting New York have for other learners of English&?
Activity 4
Now watch the film again and complete the following exercises:
Watch the interviewees answering the first question and tick the answers you hear on the list below. Be careful: there are two answers on the list below which are not mentioned in the video!
1. English is useful when speaking with tourists.
2. Computer software programs are in English.
3. English is important when traveling around the world.
4. English is useful for communicating with people from international companies.
5. An English exam certificate is necessary to graduate from universities in many different countries.
6. It is important to have certification in English to prove that you know English.
Watch the interviewees answering the second question and find out who makes the following statements:
7. ____ says that it can be difficult to find the right expressions when speaking.
8. ____ says that English grammar is very different from his/her native tongue.
9. ____ says that he/she found listening and speaking a bit hard.
10. ____ says that he/she found English grammar difficult at first.
Watch the interviewees answering the third question and correct the following statements:
11. You can improve your vocabulary and grammar outside class and hear different accents.
12. You can listen to songs in English.
13. You can speak a lot with students and hear a lot when you go outside, for example, into the street or into a shop.
14. You overcome the fear of not speaking English fluently.
15. You gain confidence and stop worrying about getting a job.
Watch the interviewees answering the third question. Put this advice in the order you hear it on the video.
A. If you can’t travel abroad, take English seriously: practice for at least 2 hour every day or do an intensive course.
B. Go to a country where English is the native language because you start thinking in that language.
C. Watch television.
D. Go to a city where everyone speaks English because you have to speak English to connect with people.
E. Talk a lot with native speakers, even if you make mistakes.
F. Practice more: speaking, accents. Get a government grant to travel if you can.
Post – watching
Activity 5
Discuss the following questions:
1. Have you ever studied English in an English-speaking country?
2. How long would you need to stay in an English-speaking country to learn to speak English fluently?
3. Do you agree with Adrian when he says that, if you can’t study abroad, it is necessary to take English seriously and practice for one or two hours every day?
4. Which is more useful for you: American English or British English? Why? Which do you find easier to understand? Why do you think so?
5. Some of the interviewees recommend watching TV in English – in what way can this help students to master the English language?
6. What can you to conquer your fear and gain confidence when speaking English?
7. What other questions do you think the film should have asked?
8. What did you find most interesting or surprising about the video?
9. If you could go abroad to study, what country would you choose?
10. If you want to learn English, is it better to study in an English-speaking country or simply to get a job there, for example, using program “Work & Travel”?
11. Is it important for engineer to speak English fluently? Why?
Activity 6
Imagine you are making a film like “Tales from America”. Interview your partner, using the questions below:
1. Would you consider going abroad to learn English? What are the advantages and disadvantages of learning English in an English-speaking country?
2. Why is learning English important for you?
3. What problems do you have learning English?
4. How would living in an English-speaking country help with these problems?
5. What tips and advice can you offer learners who are thinking of studying English abroad?
6. How can you use English in your future job?
Activity 7
Tales from America – Quiz
Try the quiz below:
1. Which word is NOT used by learners to describe their first impressions of New York?
a. big
b. beautiful
c. amazing
d. spectacular
2. According to the Israeli student, Lee, why “must” people know English?
a. English is the official language of America.
b. English is the most important language in the world.
c. English is the language used in most universities.
d. English is the language psychologists use in their profession.
3. What was the Argentinean engineer’s main reason for going to New York?
a. To learn about English software.
b. To upgrade his technical skills in English.
c. To improve his English in an English setting
d. To experience the busy life of native Americans.
4. Three of the female learners say that knowing English helps people from their own countries
a. make friends.
b. improve their own language.
c. get jobs.
d. understand each other.
5. According to the interviewees, why is it difficult for beginners to express themselves in English?
a. Beginners are afraid to talk to people.
b. Beginners don’t practice for long enough.
c. Beginners focus too much on grammar.
d. Beginners still think in their native language.
6. How is the translation student improving her English each day?
a. She is living with a native English speaker.
b. She has a teacher who uses different accents.
c. She is not afraid to ask questions.
d. She refuses to speak her native language at school.
7. What improved for the South Korean student after going to New York?
a. Her confidence in speaking English
b. Her TOEIC score
c. Her ability to make friends
d. Her courage to travel
8. What advice is given to people who can’t travel to an English-speaking country?
a. Study at least one or two hours per day.
b. Focus on reading before speaking.
c. Go to an English-only school.
d. Memorize English words online.
9. What is the last piece of advice for English learners?
a. Play in English.
b. Move to New York.
c. Practise your accent.
d. Watch TV.
10. Which of the following is true about New York based on the camera footage?
a. New York taxi drivers speak English.
b. New York is a multicultural city.
c. Teachers in New York are rarely native speakers.
d. Most people who go to New York are tourists.
Home task: write your own reasons to study English, describe the way that you prefer to study, give information about your difficulties and ideas how to overcome them.
Video 2
Song “What a Wonderful World”
Sam Cooke, James Taylor
Pre-watching
Activity 8
Match the subject and its definition:
|
1. history |
a) the language that people speak in France, Belgium, Canada and several other countries |
|
2. biology |
b) the period in European history between about the year 1000 AD and the year 1500 Ad. Things belonging to this period are described as medieval |
|
3. science |
c) the part of mathematics that studies how the angels and sides of triangles are related |
|
4. French |
d) the study of the events in the past |
|
5. geography |
e) the study and knowledge of the physical world and its behaviour that is based on experiments and proven facts and is organized into a system |
|
6. trigonometry |
f) a type of mathematics that uses letters and symbols in place of numbers |
|
7. algebra |
g) the scientific study of living things |
|
8. Middle Ages |
h) the study of the earth’s physical features and the people, plants and animals that live in different regions of the world. |
Watching
Watch the song and complete the gaps with words from the table:
What a wonderful world this would be
What a wonderful, wonderful, wonderful, wonderful world.
Don't know much about ___ (1).
Don't know much ___ (2).
Don't know much about a ___ (3) book.
Don't know much about the ___ (4) I took.
But I do know that I love you
And I know that if you love me, too
What a wonderful world this would be.
Don't know much about ___ (5).
Don't know much ___ (6).
Don't know much about ___ (7).
Don't know what this slide rule is for.
But I do know one and one is two
And if this one could be with you
What a wonderful world this would be.
What a wonderful, wonderful, wonderful, world.
Now I don't claim to be an "A" student
But I'm trying to be.
'Cause maybe by being an "A" student, baby, baby
I could win your love for me.
Don't know much about the ___ (8).
Look at the pictures and I turn the pages.
Don't know nothing 'bout no rise and fall.
Don't know nothing' 'bout nothing at all.
Girl it's you that I've been thinking of
And if I could only win your love
What a wonderful world this would be.
What a wonderful, wonderful, wonderful, wonderful world,
What a wonderful, wonderful, wonderful, wonderful world.
Unit 2
Environment
Vocabulary
Match the word and its definition:
|
Word |
Definition |
1. global warming |
a). mixture of water with sulphuric, nitric and other acids formed by gases released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned (factory smoke, cars, etc.). |
2. greenhouse effect |
b). the release or discharge into the air of pollutant substances such as gas or smoke. |
3. pollution |
c). a measure of the effect that human activities have on the climate (measured in units of carbon dioxide). |
|
4. acid rain |
d). animals and plants in danger of becoming extinct. |
|
5. deforestation |
e). a gradual increase in world temperatures caused by polluting gases such as carbon dioxide which are collecting in the air around the Earth and preventing heat escaping into space. |
|
6. drought |
f). carbon dioxide: a colorless, odorless, non-poisonous gas that is a normal part of the air. It is absorbed by plants and exhaled by humans and animals. Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, wood) increases carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming. |
|
7. fossil fuels |
g). the surroundings and external conditions that affect the growth and development of living things |
|
8. CO2 |
h). capable of being broken down or decomposed by natural biological processes. The term is used to refer to “environmentally friendly” products. Many chemicals, food scraps, cotton, wool, and paper are bio-degradable; plastics and polyester generally are not. |
|
9.endangered species |
i).
fuels that are formed in the
ground from the remains of dead plants and animals: oil, natural gas and
coal. |
|
10.greenhouse gases |
j).the act of cutting down large area of forest |
|
11. emission |
k). an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere which is believed to be the cause of a gradual warming of the surface of the Earth. |
|
12. environment |
l). gases that trap the heat of the sun in the earth’s atmosphere, producing the greenhouse effect. The result is an increase in the temperature of the earth’s surface. They include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. |
|
13.biodegradable |
m).a long period of dry weather so that there isn’t enough water. |
|
14. carbon footprint |
n). damage caused to water, air.... by harmful substances or waste. |
Video 1
“Global warming”
National Geographic
Pre – watching
Test your knowledge. Take the “Climate change” quiz:
1. Which of these is an example of climate change?
• A windy day
• A rainy day
• A hot summer day
• A sunny day
2. Where do greenhouse gases trap energy?
• In the atmosphere
• In the mountains
• In outer space
• In the soil
3. Which one of these is a greenhouse gas?
• Oxygen
• Carbon dioxide
• Nitrogen
• Sulphur dioxide
4. For how long has the Earth’s climate been changing?
• 100 years
• 1 million years
• 1 billion years
• 5 billion years
5. What is one reason why scientists think that the sea level is getting higher?
• Ships make the water higher
• Melting glaciers add more water to the sea
• The ozone hole is warming the ocean
• All of the above
6. At what time in history did humans start to add lots of greenhouse gases to the
atmosphere ?
• Ice age
• Great depression
• Industrial revolution
• Mesozoic era
7. Which one of these activities sends greenhouse gases into the atmosphere?
• Riding in a car
• Riding a bike
• Walking
• Sailing
8. What do scientists study in order to learn more about past climate?
• Sediments
• Ice
• Tree rings
• All of the above
9. Why have plants and animals been able to adapt to changes in climate in the past?
• Humans protected them from changing climate
• Past climate changes occurred slowly enough for the plants and animals to
adapt
• The climate has not changed in the past, so plants and animals did not have to adapt to a new environment
• Plants and animals always benefit from changes in climate
10. How can you help to slow global warming?
• Save electricity
• Plant trees
• Recycle
• All of the above
Watching
Activity 2
Now watch first the film about global warming. Answer the questions:
1. When has the planet’s temperature risen?
2. What reason has the temperature driven up?
3. What have factories, power plants and eventually cars burnt and release into the atmosphere?
4. Why is the Greenhouse effect being intensified?
5. What was the warmest year in measured history with 2.5 coming in second?
6. How much has Arctic sea ice declaimed in a last 30 years?
7. What kind of change do climate modules predict?
8. How do many organizations advocate reducing impact of global warming?
9. What should consumer do to help our planet?
Activity 3
Watch the film again and complete the gaps:
1. This greenhouse gases heat near the Earth through natural appearing process called ___.
2. The greenhouse effect begins with ___ and the ___ irradiates to the Earth.
3. The Earth and the atmosphere absorb some of the energy but the rest is radiated into ___ .
4. Naturally appearing gases in the atmosphere trap some of the energy and reflected back warming ___.
5. Researchers predict that temperature will increase about ___ to ___ by the end of the century.
6. Weather pattern could change making ___ more frequent.
7. Severe ___ could be more coming in more areas and ___ are unable to adapt.
Activity 4
Compare and contrast two pictures. Explain the process of Natural Greenhouse effect and Enhanced greenhouse effect. Use information from film.
Natural greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is an indispensable natural phenomenon; without it, the average temperature, currently 59°F, would be no higher than 0°F.
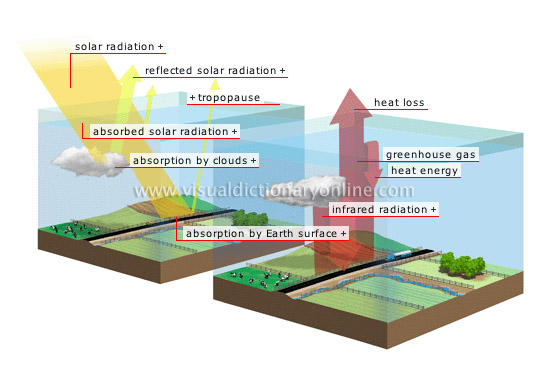
Enhanced greenhouse effect
Human activity constantly emits greenhouse gases, which trap ever more heat in the atmosphere.
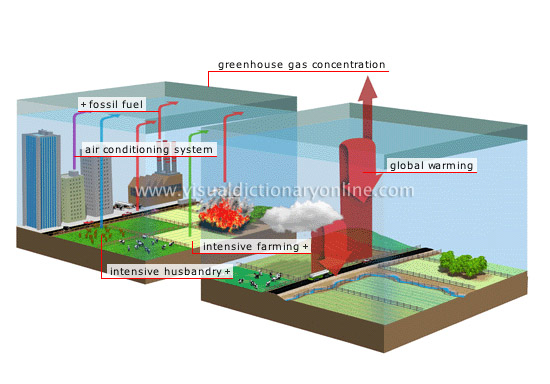
Video 2
“The Reality of Global Warming”
Pre – watching
Activity 1
Answer the questions:
1. Why is our Earth in a state of crisis?
2. What are the consequences?
3. What will more catastrophic events occur if we continue to live this way?
4. What should we do to preserve our planet?
Watching
Activity 2
Watch the video and match two parts of the sentences:
Consequence of Earth’s crisis:
|
1. Our glaciers… |
a) are rising. |
|
2. Our cities… |
b) are intensifying. |
|
3. The climate … |
c) is increasing. |
|
4. Our lakes … |
d) is upsetting the balance of nature. |
|
5. Our ocean’s temperature … |
e) are melting. |
|
6. Hurricanes… |
f) are drying up. |
|
7. Rainfall … |
g) are facing the treat of extinction. |
|
8. Record setting heat temperatures |
h) is changing. |
|
9.Global warming … |
i) are at a dangerous level. |
|
10. Many species … |
j) are flooding. |
Activity 3
Watch the video again and complete the sentences with suitable verbs:
What measures we should take:
1. Always ___ to recycle and reuse.
2. ___ alternative energy methods.
3. ___ the power and ___ your household energy.
4. ___ your litter.
5. Reusable bags ___ thousands of plastic bags from ending up in landfill per year.
6. ___ more environmentally-friendly dealing products around your home.
7. ___ low or zero emission vehicles to get you where you need to go.
8. ___ using public transport more often or try car pooling.
9. ___ we only have one planet.
10. And it’s depending on you to ___ a difference.
Post – watching
Activity 4
Work in pairs. Answer the questions:
1. Is global warming just a myth to scare people, as some people say? Why/not?
2. Will humans become extinct because we have irreparably ruined the environment?
3. What environmental problems have you heard about in the news recently?
4. If temperatures continue to rise year after year, how will our lives be different in the near future? How about long term, say 100 years from now?
5. What do you do (or have you done) to reduce global warming? Please explain.
6. Could you do more to reduce global warming and protect the environment?
7. Should the government or the people bear the brunt for environmental protection?
8. What are five ways that every person can help the environment, starting now?
Video 3
Song
Michael Jackson
“Save our planet”
Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. What is Brazil responsible for?
2. What makes Brazil the 4th country that emits CO2 in the world?
3. What are environmental problems mentioned in video?
5. What solutions does Michael Jackson suggest?
Activity 5
Look at the picture how to protect our environment. Do you accept each way? Explain advantages of each point.
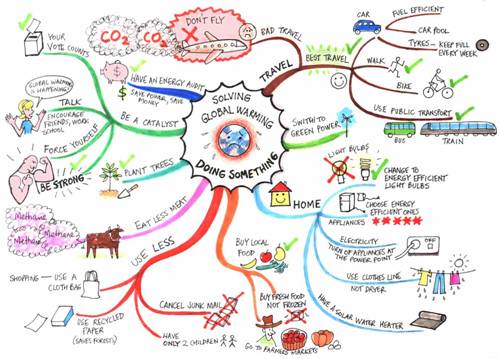
Home task: write article about main type of pollution in Almaty. What should we do to stop pollution? What happen if we continue to pollute our city?
Unit 3
Alternative energy sources
Pre – watching
1. Match the word and its definition:
|
a) Fossil fuels |
1) comes from the heat of the sun. You can use panels to trap the energy and it can be saved for cloudy days. |
|
b) Nuclear energy |
2) comes from the heat inside the earth. It is good for places with volcanic activity. |
|
c) Solar energy |
3) takes energy from flowing water such as rivers, streams and ocean currents. |
|
d) Wind energy |
4) are extracted from the earth such as coal, oil and natural gas. When they are burned to make energy they produce carbon dioxide which contributes to global warming. |
|
e) Geothermal energy |
5) produces energy by moving blades on a turbine or mill. It is clean energy but it can make a lot of noise. |
|
f) Biomass energy |
6) is produced from plant or human waste. Wood is the most common source but now methane gas or vegetable oils are being used to create energy. |
|
g) Hydroelectric energy |
7) is produced by splitting atoms. There is a risk of accidents and this form of energy produces dangerous waste that is difficult to dispose of. |
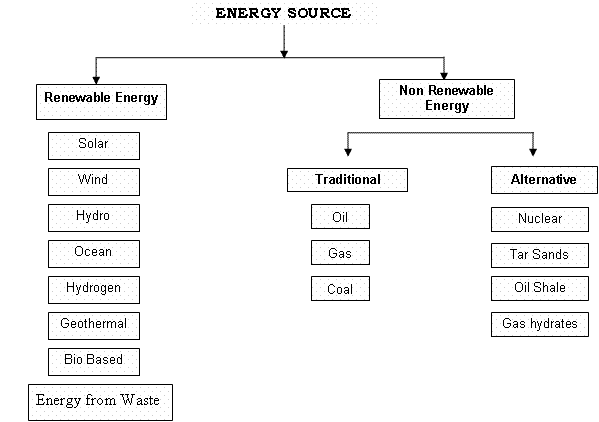
2. Brain storm. Watch the video:”Energy conversation rap” Draw the scheme: renewable and non renewable sources of energy. What do you remember about each of them?
Watching. We are going to watch the video:”Alternative energy sources”. Before watching draw the table:
|
Type of alternative energy |
Device we use to catch (trap) energy |
Main principle to turn this type of energy into electricity |
Application |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a) Watch the movie and complete the first column of the table: solar, wind hydro energy.
b) Watch the movie again and complete second column of the table: solar panel, wind turbines, hydroelectric dam
c) Watch the movie look at the schemes and complete third column of the table: sun heats solar panel etc.
d) Watch the movie again and complete fourth column of the table: sun – street lights, car etc.
e) Watch the movie “Geothermal energy and complete the last line in the table.
Post – watching
1.Reading. Read the text:”Non – traditional renewable sources of energy”. Answer the questions:
a) Why is it important to develop non – traditional sources of energy?
b) What is the consumption of traditional power sources per year?
c) How can scientists transform solar energy into electricity?
d) How can engineering improve the efficiency of solar power station?
e) Explain main principle of thermal-chemical cycle
f) Where are geothermal power stations operated?
2. Scan each paragraph and find appropriate information for our table
Solar energy
Watch the video: ”How do solar energy panel works” and study the facts about solar energy. Add information in your table:
▪ Sunlight contains electromagnetic energy. This energy can be changed into electrical energy by photovoltaic cells.
▪ These cells are made of a material called silicon. When this material is exposed to sunlight an electric current can be produced. This is how a calculator works.
▪ The sun’s energy can be used to heat homes, to power cars, weather stations, and even satellites.
Main principle of using solar energy
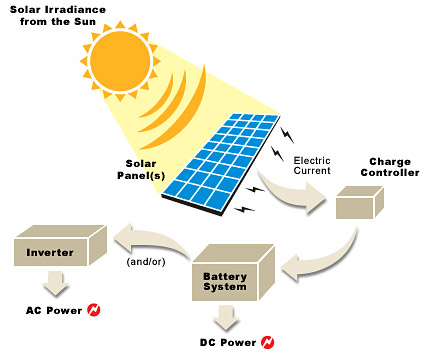
Watching
Wind energy. “Wind farm”
Watch the video and study the facts about using wind energy. Add information in your table:
▪ a windmill that produces electricity is called a wind turbine, or a wind energy converter (WEC). Wind turbines are much larger than windmills, over 39 meters high.
▪ the wind changes direction all the time, so the top of the turbine rotates round so that the wind can always spin the blades. The box behind the blades contains the turbine. As the blades turn the turbine spins a shaft which spins the generator which produces electricity.
▪ a group of wind turbines is called a wind farm.
Main principle of using wind energy
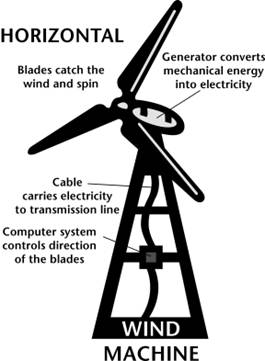
Water energy
Study the information about hydroelectric station:
▪ in hydroelectric stations, water is stored in reservoirs or behind dams. Water flows downhill through large pipes and through the turbines. The falling water turns the turbines, spins the shaft, and turns the generator to make electricity, simple! The larger the river the more energy can be harnessed, so in some parts of the world large rivers are used by Hydro Power Stations to make electricity.
Main principle of using hydro energy
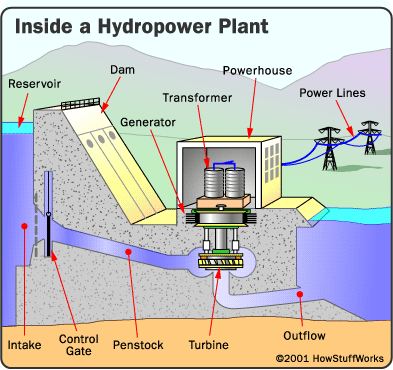
Watching
Video
“Geothermal energy”
Watch the video. Add information in your table. Study the main principle how geothermal power station works:
Geothermal Power Station
Step 1 – A deep hole or well is drilled down into the reservoir of steam or hot fluids.
Step 2 – Cool water is pumped down through a pipe, where it is heated by the hot fluids.
Step 3 – The steam produced is released at the surface and used to drive a turbine generator to make electricity.
Step 4 – The geothermal water (the water from inside the earth) is then pumped back down the bore hole to be reheated by the earth.
Main principle of using geothermal energy
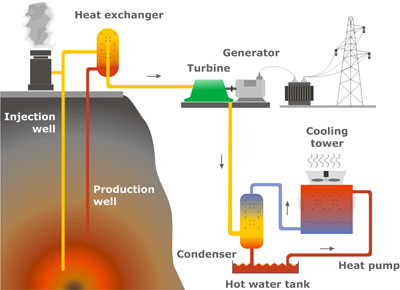
1.Work in pairs. Describe each type of alternative energy according to their features. Name advantages and disadvantages.
2.Discussion. Decide what type of energy is suitable for each city of Kazakhstan. Explanation should be based on facts from the table.
3.Home task: write story: what type of alternative energy will be better to use in your native city. Use such structure: If I were mayor of our city I would …
Unit 4
Television
Pre – watching
Activity 1
Test your knowledge. Take the “History of television” quiz:
1. German, Paul Nipkow developed a rotating-disc technology to transmit pictures over wire in ____ called the Nipkow disk. Paul Nipkow was the first person to discover television’s scanning principle, in which the light intensities of small portions of an image are successively analyzed and transmitted.
a) 1800
b) 1856
c) 1884
2. In the 1920’s, John Logie Baird patented the idea of using arrays of transparent rods to transmit ___ for television. Baird’s 30 line images were the first demonstrations of television by reflected light rather than back-lit silhouettes. John Logie Baird based his technology on Paul Nipkow’s scanning disc idea and later developments in electronics.
a) sound
b) light
c) images
3. Charles Jenkins invented a ___ television system called radio vision and claimed to have transmitted the earliest moving silhouette images on June 14, 1923.
a) mechanical
b) analogue
c) digital
4. Electronic television is based on the development of the cathode ray ___, which is the picture tube found in modern TV sets. German scientist, Karl Braun invented the cathode ray tube oscilloscope (CRT) in 1897.
a) screen
b) tube
c) remote control
5. Russian inventor, Vladimir Zworykin invented an improved cathode-ray tube called the ___ in 1929. The kinescope tube was sorely needed for television. Zworykin was one of the first to demonstrate a television system with all the features of modern picture tubes.
a) stethoscope
b) kinescope
c) telescope
6. In ___, Philo Farnsworth was the first inventor to transmit a television image comprised of 60 horizontal lines. The image transmitted was a dollar sign. Farnsworth developed the dissector tube, the basis of all current electronic televisions. He filed for his first television patent in this year.
a) 1920
b) 1927
c) 1939
7. Louis Parker invented the modern changeable television ___. The patent was issued to Louis Parker in 1948.
a) receiver
b) transmitter
c) aerial
8. Color TV was by no means a new idea, a German patent in 1904 contained the earliest proposal, while in 1925 Zworykin filed a patent disclosure for an all-electronic color television system. A successful color television system began commercial ___, first authorized by the FCC on December 17, 1953 based on a system invented by RCA.
a) sending
b) receiving
c) broadcasting
9. Cable television, formerly known as Community Antenna Television or CATV, was born in the mountains of Pennsylvania in the late 1940’s. The first successful color television system began commercial broadcasting on December 17, ___ based on a system designed by RCA.
a) 1942
d) 1953
c) 1966
10. It was in June of ___, that the TV remote controller first entered the American home. The first TV remote control called “Lazy Bones,” was developed in 1950 by Zenith Electronics Corporation (then known as Zenith Radio Corporation).
a) 1955
b) 1956
c) 1957
11. The very first prototype for a plasma display monitor was invented in 1964 by ___ .
a) Philo Farnsworth
b) Vladimir Zworykin
c) Donald Bitzer, Gene Slottow, and Robert Willson.
12. Web TV was rolled out in 1996
a) 1985
b) 1996
c)2000
Activity 2
Match the word and its definition:
|
1. pixels |
a) is really a three-part invention: the TV camera that turns a picture and sound into a signal; the TV transmitter that sends the signal through the air; and the TV receiver (the TV set in your home) that captures the signal and turns it back into picture and sound. |
|
b) is a television system that has more lines per picture than present systems, and thus produces much sharper images. At present American TV has 525 lines per image and European TV 625 |
|
|
3. vacuum tube |
c) on a TV screen with standard aspect ratio (4:3), these videos appear with horizontal black bars above and below the image. This is a method for displaying the entire picture, as seen in a movie theater. |
|
4.analog |
d) are millions of tiny picture elements. Each element is made up of three smaller red, green, and blue sub-elements. The more these elements in an image, the greater the resolution. |
|
5. television |
e) is the transmission of TV programs into the home and office via coaxial cable. |
|
6. LCD (liquid-crystal display) televisions |
f) refers to an aspect ratio of 16:9, which is the optimum viewing ratio for DTV and HDTV broadcasts. Traditional TV sets have an aspect ratio of 4:3. |
|
7.high definition TV or HDTV |
g) is relating to data in the form of numerical digits. Describes a new, more efficient method of storing, processing and transmitting information through the use of computer code. |
|
8. plasma screen or”gas discharge display” |
h) using radio waves to distribute radio or TV programs which are available for reception by the general public. |
|
9.cable TV |
i) is an old-style television makes a picture using three electron guns. |
|
10. widescreen |
j) A device built-in to a TV that allows reception of analog broadcasting. |
|
11. broadcasting |
k) Flat-panel TV that ranges from 15 to 65 inches They have millions of tiny picture elements called pixels that can be switched on or off electronically to make a picture. |
|
12. digital |
l) is relating to a mechanism in which data is represented by continuously variable physical quantities (such as voltages). |
|
13. Letterboxed video |
m)is a flat-screen technology that uses tiny cells lined with phosphor that are full of inert ionized gas (typically a mix of xenon and neon). Three cells make up one pixel (one cell has red phosphor, one green, one blue). |
|
14. NTSC Tuner |
n) Amount of detail that can be seen in a broadcast image (amount of lines and dots (pixels) that make up an image). Typically, the higher the number of lines or pixels, the sharper and more detailed the picture will be. |
|
15. resolution |
o) is an electron tube evacuated to a high degree of vacuum. |
Watching
Draw the table. Complete the table with information from previous tasks. During the watching complete each column of table.
|
Type of TV |
Date of invention/ inventer |
parts |
Main principle of working |
advantages |
disadvantages |
|
Analog |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Digital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDTV |
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 3
“How TV works”
Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. How many years has the basic technology been getting better?
2. How many important parts are there in TV set?
3. How images to be displayed?
4. How many electron beams does the electron gun produce?
5. What happen when electron beam heats the screen?
6. How many pixels are there in a typical television screen?
7. What are the steering coils in charge of?
8. Watch the video again and add information in the table.
Activity 4
“How cable TV works”
Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. Where does cable TV star?
2. How do network set our programs?
3. How many programs and heart channels do cable companies take?
4. What device do cable company use to push the long way signal?
5. What device should we use to get 800 channels?
6. Why do cable companies shrink network signal?
7. What is digital cable?
Watch the video again and add information in the table.
Activity 5
“How HDTV works”
Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. How much does normal television cost?
2. How much does HDTV cost?
3. What is picture on TV sets formed by? How is it called?
4. What is the resolution of normal TV set?
5. What is the resolution of HDTV set?
6. How many connections are there in the back of a digital television sets?
7. What is the third big difference between normal TV set and HDTV?
8. What is function of a separate receiver in HDTV set?
Watch the video again and add information in the table.
Activity 6
Read the text 4A “Television” in your books. Complete missing information in your table.
Work in pairs. First student speaks about analog and cable TV, second about digital and HDTV.
Discussion. Decide what type of television will be in future and why. Explanation should be based on facts from the table.
Home task: write story: what type of TV sets was the most important for mankind.
Unit 5
Computers
Pre – watching
Activity 1
Write the list of words concerned with computer. Watch the video: “Computer vocabulary” and check your answer.
What parts of the computer do you know? Look at the picture and match word or collocation with its definition
Handheld computer
Small portable computer with a miniature operating system; it is used mostly for personal management tasks (agenda, address book).
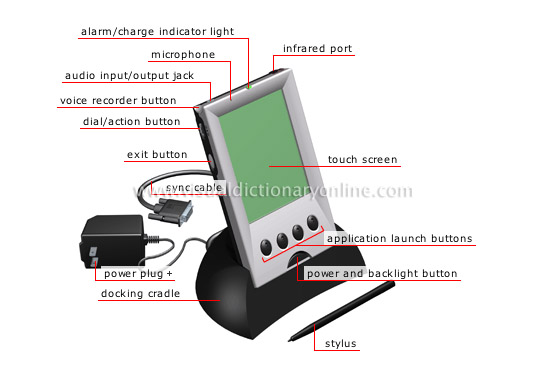
|
Word/collocation |
definition |
|
1. audio input/output jack |
a) Thumb wheel used to validate a selection or to scroll up and down through a document. |
|
2. voice recorder button |
b) Liquid crystal display that is sensitive to the touch and the motion of a finger or stylus. |
|
3. dial/action button |
c) Small light that signals an alarm or indicates that a battery is being charged. |
|
4. exit button |
d) Key used to turn a computer on or off; it also illuminates the screen in poor lighting conditions. |
|
5. sync cable |
e) Pencil like implement used to enter data or to select an option on a touch screen. |
|
6. power and backlight button |
f) Connector used to transfer audio signals between the computer and a sound recording or reproduction device such as a microphone or headphones. |
|
7. application launch buttons |
g) Base in which a handheld computer is placed to recharge its battery or exchange data with another computer. |
|
8. infrared port |
h) Cable that connects the docking cradle to the computer; it allows data to be exchanged between the two devices. |
|
9. alarm/charge indicator light |
i) Device that converts electric pulses into broadcast or recorded sounds. |
|
10. microphone |
j) Keys used to directly access available applications such as word processing and Internet browsing. |
|
11. touch screen |
k) Key used to record a brief voice message. |
|
12. stylus |
l) Device that uses infrared signals to exchange data with a device with a similar port (a network access transmitter-receiver, computer, printer). |
|
13. docking cradle |
m) Key used to exit an application. |
Watching
Video 1
“History of Computers – video: Intel Education: the Journey inside: Lesson 1: History of computers”
Activity 2
Watch the video and complete the gaps:
Throughout time, humans have invented ingenious [inʹʤi:niəs] (замысловатый) calculating ___ (1). One of the earliest was the abacus [ʹæbəkəs] (счеты). It’s about ___ (2)years old. Mechanical calculators that could add (+) and multiply (x) (but not subtract! (-)) were invented in the 1600s. In ___ (3), Charles Xavier Thomas de Colman invented the arithmometer, a machine that could add (+), subtract (-), multiply (x) and divide (;). It was Charles Babbage though, in the early 1800s, who designed mechanical calculating machines that were the true ancestor of today’s ___ (5). Ada Byron King was his programmer and today is considered the mother of computer programming.
Babbage’s design for his ultimate (last) ___ (5), the Analytical Engine, was never produced. It did anticipate the four components essential to modern computing. These components are input, storage, processing and output. The problem with Babbage’s and other mechanical calculators was just that—they were ___ (6). The moving parts they relied on were slow and subject to breakdown.
What made modern computers possible was the invention of something that could do calculations and other information processing with no moving parts and do it very ___ (7). That something was electronic components. With electronic components, a fast and efficient machine such as Babbage proposed could be built with all four components essential to modern computing.
Activity 3
1. Find words in the text to mach these definitions:
a) an object used for counting or doing simple calculations, consisting of a frame with small balls in a row
b) to put numbers or amounts together to calculate their total
c) to take a number or amount from another number or amount
d) to add a number to itself a particular number of times
e) to do a mathematic calculation to find out how many times a number contains a smaller number
f) to think that something will probably happen (syn. Foresee)
g) information that is put into a computer or a piece of electronic equipment using another machine such as a keyboard or microphone
h) the ability of a computer to keep information or the process of doing this
i)to put information into a computer in order to organize it
g) the information shown on a screen or printed on paper by a computer
Activity 4
Watch the video again and answer the questions:
1. What was the earliest calculating machine?
2. When were mechanical calculators invented?
3. What kind of machine was arithmometer?
4. Who designed mechanical calculating machines? When?
5. Who is the mother of computer programming?
6. What are the four components of modern computer? Who anticipated them?
7. What was the problem with Babble’s computer?
8. What invention made modern computers possible?
Video 2
“Four Components of a Computer – video: Intel Education: The Journey inside: Lesson 2: Four components of a computer”
Activity 5
Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. What does computer process?
2. What are the four components of computer processing?
3. What does software give the computer?
4. What is microprocessor?
5. What device is more sophisticated? Why?
Activity 5
Watch the video again and complete the table:
Computer and toaster: similarities and difference
|
|
Computer |
Toaster |
|
process |
|
|
|
physical parts (hardware) |
|
|
|
software |
|
|
|
microprocessor |
|
|
Video 3
“How Computers Get Input – video: Intel Education: The Journey Inside: Lesson 3: How Computers Get Input”
Activity 6
Watch the video and tell are there statements True or False:
1. Computer can download information like numbers, text, pictures, and even music.
2. Using the computer, it’s easy to print words.
3. Input devices are used to storage information in your computer.
4. You type a sentence on your screen and it goes into the computer.
5. You speak into a system unit and your computer records your words.
6. You make funny faces at the video camera and your computer draws every one of them.
Video 4
“How Computers Store Information – video: Intel Education: The Journey Inside: Lesson 4: How Computers Store Information”
Activity 7
Watch t the video and match two parts of the sentences:
|
1. When you use a telephone, |
a) Hard drives, Optical Discs, storage, and Removable Media. |
|
2. To process information, |
b) information actively being used for processing. |
|
3. Computers store the information you give them, |
c) a type of memory that does not accept new information. |
|
4. To store all this, |
d) temporary storage. |
|
5. Temporary storage is for |
e) it does not store information. |
|
6. Random Access Memory (RAM) accepts new information for |
f) they use two basic kinds of storage. |
|
7. Long-term storage is for information computers |
g) instructions from the software you’re using, plus the instructions they need to operate. |
|
8. These instructions are stored in read only memory (ROM), |
h) use again and again, such as the instructions the computer prepares itself with every time you turn it on. |
|
9. Computers also use a variety of devices to store information that isn’t actively being used for processing: |
i) computers need to be able to store it. |
Video 5
“How Computers Process Information – video: Intel Education: The Journey Inside: Lesson 5: How Computers Process Information”
Activity 8
Watch the video and choose the correct answer:
1. The ___ makes the computer work.
a) monitor
b) key board
c) processor
2. All ___ have to pass trough it.
a) dates and instructions
b) pictures and movie
c) software
3. It performs tasks called by software and communicates with the rest of the computer to the ___.
a) mouse
b) motherboard
c) system unit
4. In fact the history of the processor is really just a story about ___ it.
a) turn on
b) switch
c) turn off
5. Early computer processor information was ___ switchers like this.
a) hundreds
b) thousands
c) millions
6. Vacuum tubes were ___ .
a) light and tiny
b) middle size
c) big, bulky and hard
7. In unit was ___ of all.
a) 500
b) 800
c) 900
8. In 1970s the processor in function of the computer has been put into a ____.
a) motherboard
b) software
c) a single chip
9. ___ used to be programmed to perform many different tasks.
a) microprocessor
b) hard disk
c) floppy disk
10. Since ___ microprocessor has been made much smaller and much powerful.
a) 1950s
d) 1960s
c) 1970s
Video 6
“How Computers Deliver Information – video: Intel Education: The Journey Inside: Lesson 6: How Computers Deliver Information”
Activity 9
Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. What are three ways to output information from the computer?
2. What can you output on monitor?
3. What can you print?
4. What can you output through sound?
Video 7
“Which is Smarter - Human Brain or Computer? – Video: Intel Education: The Journey Inside: Lesson 7”
Activity 10
Answer the question: which is smarter: human brain or computer? Draw the table and give your prediction according to each point:
|
|
HUMAN BRAIN |
COMPUTER |
|
How it works |
|
|
|
Speed |
|
|
|
Tiredness |
|
|
|
Memory |
|
|
|
Ability to make well- reasoned decision |
|
|
|
Ability to think original thoughts |
|
|
Watch the video and compete the table.
Work in pairs. First point of view: computer is smarter than human brain. Second point of view: human brain is smarter than computer. Each student should defend one point of view using arguments from the table and his own ideas.
Video 8
“Computers of the future”
Activity 11
Watch the video and complete the gaps:
1. Pen PC is capable of storing terabytes of ___ (1), far exceeding the capacity of today’s hard disks.
2. A docking stands holds the PEN PC in ___ (2).
3. Using lasers and infrared technology, the PEN PC projects a ___ (3) on the wall.
4. It also projects a full-size ___ (4) onto any flat surface.
5. As you type on the laser projection, it analyzes what you are typing by the coordinates of that ___ (5).
6. The virtual keyboard can be customized to any ___ (6), configured with additional keys + virtual touchpad.
7. E – fingerprinting allows only the owner to activate the PEN PC. So if you loose it, no one else can access the data. But how do you ___ (6) the data?
8. Backups of all your data can be stored in a watch fitted with a holographic storage ___ (8).
9. Wireless Bluetooth ___ (9) transfers data from the PEN PC to your watch.
10. In 2020 physical keyboards and monitors will be a thing of the ___ (10).
11. The Pen PC will be the ultimate in a truly portable ___ (11).
12. The virtual keyboard is already in the market for certain ___ (12) and PDAs.
Post-watching
Activity 11.
We are at the scientific conference devoted computers. Open you book at page 205 ex 5. Read the clichés. One student is a chairman. Other students should prepare information according to each video and introduce their reports. Speech should be based on facts from the activities.
Home task: write essay: importance of computers in our life.
Unit 6
Materials
Video
“Are Carbon Nanotubes the Next Asbestos?’
Pre watching
Activity 1
What do you know about the material “carbon nanotubes”? Test your knowledge. Take this quiz:
1. Carbon nanotubes are extremely thin. Their diameter is about ___ times smaller than a human hair.
a) 1,000
b) 10,000
c) 100,000
2. Carbon nanotubes are hollow ___ made of carbon atoms.
a) cylinders
b) sphere
c) cube
3. Nanotubes, depending on their structure, can be metals or ___.
a) conductor
b) semiconductor
c) insulator
4. Carbon nanotubes are also extremely strong materials and have good ___ conductivity.
a) electrical
b) thermal
5. Researchers ___.
a) have continued to look for ways to use them
b) studied them properly
6. The newly-discovered ability of carbon nanotubes to serve as ___ sources has great potential.
a) proton
b) photon
c) electron
7. Carbon nanotubes have great significance for use in
a) flat-panel displays
b) microwave generators
c) devices for electric surge protection
d) high intensity lamps
e) all of them
Watch the video and check your answer.
Watching
Activity 2
Watch the video and complete the gaps:
1. Carbon nanotubes are long, thin cylinder of ___ roughly 10,000 times smaller than the width of human hair.
2. These molecular scale tubes are stronger than ___ yet lighter than ___ and today, they are being developed for use in a variety of consumer products.
3. But under a microscope, carbon nanotubes look similar to asbestos ___ leading scientists to believe that they could cause similar health problems.
4. Asbestos fibers are very long, needle-like structures compared to most other ___ that we inhale in the lung which are round and easy to clear from the lung.
5. Now if it a longer type of structure more like this ___ ___ this would be more the dimensions of an asbestos fiber or a nanotube even though a nanotube would be much thinner.
Activity 3
Watch the video again and answer the questions:
1. What areas does nanotechnology bring new advances and discoveries?
2. What did asbestos turn out to be instead of revolutionizing the world?
3. What does asbestos cause?
4. What is the subject of Dr Jamie Bonner’s research?
5. Why do scientists believe that carbon nanotubes could cause similar heals problem as asbestos?
6. Should public be concerned about the field of nanotechnology?
Activity 4
Watch the video third time. Work in pairs. Student A: speak about advantages of carbon nanotube technology, student B about disadvantages. After working in pairs whole group should discuss the problem: is it worth developing technology of carbon nanotubes or it will be better to refuse from it because of the health problems?
Video
“New materials technology development”
Pre-watching
Activity 5
Have you ever heard about material “Kevlar”? Try this quiz and anticipate the answer from the video:
1. What is Kevlar?
a) a super-strong plastic
b) a super-strong metal
c) a super-strong metal ceramic compound
2. Kevlar's amazing properties are partly due to its chemical structure (how the atoms in its molecules are arranged) and partly due to the way it's made into ___ that are knitted tightly together.
a) atoms
b) fibers
c) molecules
3. Kevlar comes in two main varieties called ___ and ___ (other varieties are made for special applications).
a) Kevlar 1 and Kevlar 2
b) Kevlar 15 and Kevlar 20
c) Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49
4. Synthetic materials ___.
a) grow on plants
b) come from animals
c) are made in a chemical laboratory
5. There are two main stages involved in making Kevlar. First you have to produce the basic ___ from which Kevlar is made (a chemical called poly-para-phenylene terephthalamide—no wonder they call it Kevlar). Second, you have to turn it into strong fibers.
a) metal
b) plastic
c) compound
6. Kevlar can be used by itself or as part of a composite material (one material combined with others) to give added ___.
a) lightness
b) softness
c) strength
7. Kevlar is a plastic strong enough to stop bullets and knives.
a) True
b) False
8. Kevlar is often described as being "five times stronger than steel on an equal weight basis".
a) True
b) False
Watch the video and check your answer.
Watching
Activity 6
Watch the video again and tell if there statements True or False. To prove your statement use information and examples from video:
Kevlar fibers possess the following properties:
1. High tensile strength (five times stronger per weight unite than steel);
2. Low modulus of elasticity;
3. Very low elongation up to breaking point;
4. High weight;
5. High chemical inertness;
6. Very low coefficient of thermal expansion;
7. High Fracture Toughness (impact resistance);
8. Low cut resistance;
9. Textile processibility;
10. Flame resistance.
11. The disadvantages of Kevlar are: ability to absorb moisture, difficulties in cutting, low compressive strength.
Activity 7.
Read this extract, watch the video and give extension information:
What's Kevlar used for?
Kevlar can be used by itself or as part of a composite material (one material combined with others) to give added strength. It's probably best known for its use in bulletproof vests and knifeproof body armor, but it has dozens of other applications as well. It's used as reinforcement in car tires, in car brakes, for boatbuilding, in the strings of archery bows, and in car, boat, and even aircraft bodies. It's even used as a tough, durable building material.
Post watching
Using all information complete the table:
|
|
Kevlar |
Similarities |
Carbon nanotubes |
|
Structure |
|
|
|
|
Properties |
|
|
|
|
Application |
|
|
|
|
Advantages |
|
|
|
|
Disadvantages |
|
|
|
Discussion. We are at scientific conference. Each student should choose one point from the table and give all information. Find similarities and differences between two materials. Give prediction about future application of these new materials.
Home task: presentation. Find information about other new materials. Prepare the presentation in Power point.
Keys
Unit 1
Activity 1(Warmer)
1. False (It is the 4th largest country in the world after Russia, Canada and China).
2. False (Washington DC is)
3. True
4. True
5. False (There are 50 states and the District of Columbia, a special federal area where the capital of the country is situated).
6. The first American President was George Washington.
Activity 2
|
Interviewee |
Nationality |
Occupation |
Why is she/he in the USA? |
|
Lee Nitel |
Israeli |
Student |
For a university course she will start next month in her own country. |
|
Aneta Kaint |
Australian |
Student |
To learn English to do yoga teacher training |
|
A Rum Yang |
South Korean |
Student |
To feel closer to native speakers. |
|
Adrian Petrov |
Argentinian |
Engineer |
To improve his English in an English setting |
Activity 4
1. True; 2. True; 3. Not mentioned; 4. True; 5. Not mentioned; 6. True
7. Aneta 8. Lee 9. Carolina 10. Adrian
11.You can improve your vocabulary and LISTENING outside class and hear different accents.
12. You can WATCH TV in English.
13. You can speak a lot with NATIVE SPEAKERS and hear a lot when you go outside, for example, into the street or into a shop.
14. You overcome the fear of not UNDERSTANDING THE LANGUAGE.
15. You gain confidence and stop worrying about MAKING GRAMMAR MISTAKES.
16. Answers: 1.B 2.D 3.F 4.A 5.E 6.C
Activity 7
1b, 2b, 3c, 4c, 5d, 6a, 7a, 8a, 9d, 10b
Activity 8
1D 2G 3E 4A 5H 6C 7F 8B
Unit 2
Vocabulary
1E 2K 3N 4A 5J 6M 7I 8F 9D 10L 11b 12G 13H
Activity 1
Climate change quiz
Answers – Correct answer is underlined
1 Which of these is an example of climate change?
• A windy day
• A rainy day
• A hot summer day
• A sunny day
2 Where do greenhouse gases trap energy?
• In the atmosphere
• In the mountains
• In outer space
• In the soil
3 Which one of these is a greenhouse gas?
• Oxygen
• Carbon dioxide
• Nitrogen
• Sulphur dioxide
4 For how long has the Earth’s climate been changing?
• 100 years
• 1 million years
• 1 billion years
• 5 billion years
5 What is one reason why scientists think that the sea is getting higher?
• Ships make the water higher
• Melting glaciers add more water to the sea
• The ozone hole is warming the ocean
• All of the above
6 At what time in history did humans start to add lots of greenhouse gases to
the atmosphere?
• Ice age
• Great depression
• Industrial revolution
• Mesozoic era
7 Which one of these activities sends greenhouse gases into the atmosphere?
• Riding in a car
• Riding a bike
• Walking
• Sailing
8 What do scientists study in order to learn more about past climate?
• Sediments
• Ice
• Tree rings
• All of the above
9 Why have plants and animals been able to adapt to changes in climate in the
past?
• Humans protected them from changing climate
• Past climate changes occurred slowly enough for the plants and
animals to adapt
• The climate has not changed in the past, so plants and animals did not have
to adapt to a new environment
• Plants and animals always benefit from changes in climate
10 How can you help to slow global warming?
• Save electricity
• Plant trees
• Recycle
• All of the above
Activity 2
1. In a last century the planet’s temperature has risen unusual past about 1.2 to 1.4˚F.
2. Scientists believe its human activity that has driven the temperature up.
3.Ever since the industrial revolution began factories, power plants and eventually cars have burnt fossil fuel such as oil and coal and release huge amount of carbon dioxide and other gases into the atmosphere.
4. Scientists now believe that the Greenhouse effect is being intensified by extra greenhouse gases that human have released.
5. Scientists record that 1991 was the warmest year in measuring history with 2.5 coming in second.
6. According to NASA studies expended of Arctic sea ice has declaimed in about 10% in a last 30 years.
7. Some climate models predict settle changes others forecast sea level could flood coastal areas around the world.
8. Many organizations advocate cutting greenhouse gas emission to reduce impact global warming.
9. Consumers can help by saving energy around the house, switching the compact or receive light bulb and driving pure mills in the car.
Activity 3
1.The Greenhouse effect
2.sun, energy
3.space
4.the Earth
5.2, 10˚F
6.hurricanes
7.drought, species
Video 2
Activity 2
1E 2J 3H 4F 5A 6B 7C 8I 9D 10G
Activity 3
1.remember
2.consider
3.save
4.reduce
5.save
6.use
7.use
8.consider
9.remember
10.make
Unit 4
Pre – watching
Activity 1 Quiz
1C 2 C 3A 4B 5B 6B 7A 8C 9B 10B 11C 12B
Activity 2
1D 2I 3N 4L 5A 6K 7B 8M 9E 10F 11H 12G 13C 14J 15N
Unit 5
Pre – watching
Activity 1
1F 2K 3A 4M 5H 6D 7J 8L 9C 10I 11B 12E 13G
Activity 2
1.machines
2. 5,000
3.1820
4.computers
5.calculator
6.mechanical
7.fast
Activity 3
1.abacus
2.add
3.subtract
4.multiply
5.divide
6.anticipate
7.input
8.storage
9.processing
10.output
Activity 7
1E 2I 3G 4F 5B 6D 7H 8C 9A
Activity 8
1C 2A 3B 4B 5B 6C 7B 8C 9A 10C
Activity 11
1. data
2. place
3. screen
4. keyboard
5. location
6. size
7. recover
8. unit
9. technology
10. past
11. computer
12. cell phones
Unit 6
Materials
Activity 1
1B 2A 3B 4B 5A 6C 7C
Activity 2
1. carbon
2. steel, aluminum
3. fibers
4. particles
5. computer cable
Activity 5
1A 2B 3C 4C 5B 6C 7A 8A
Activity 6
1T 2F 3 T 4F 5T 6 T 7T 8F 9T 10T 11T